Context
World Down Syndrome Day (WDSD) is observed every year on 21 March. It is a global campaign that is observed annually to spread awareness about Down Syndrome.
History
- The first World Down Syndrome Day was observed in 2006.
- Then the Brazilian Federation of Associations of Down Syndrome worked with Down Syndrome International and its members to launch an extensive campaign to generate international support.
- In November 2011, the General Assembly adopted a resolution by consensus to celebrate World Down Syndrome Day every year.
- The next month it declared March 21 as World Down Syndrome Day.
Theme 2022
- “Inclusion Means”. It calls for making efforts to include people with down syndrome in all matters of life and not discriminate against them.
About Down Syndrome
- Down syndrome occurs when an individual has an extra partial (or whole) copy of chromosome 21.
- A baby is typically born with 46 chromosomes. Down Syndrome babies have an extra copy of one of these chromosomes.
- Trisomy is a medical term for having an extra copy of a chromosome.
- Trisomy 21 is another name for Down Syndrome.
- It is not yet known why this syndrome occurs, but Down syndrome has always been a part of the human condition.
- It exists in all regions across the globe and commonly results in variable effects on learning styles, physical characteristics and health.
- Babies with Down Syndrome have an extra copy of a chromosome, which changes how the baby’s body and brain develop.
- People with this syndrome usually have an IQ (a measure of intelligence) in the moderately low range and are slower to speak than other children.
| Normal Human Karyotype |
Down Syndrome Karyotype |
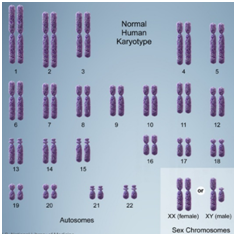 |
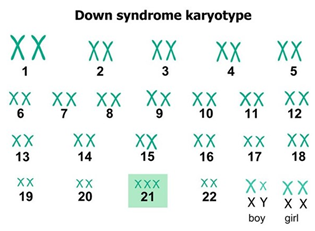 |
Chromosome
- In the nucleus of each cell, the DNA molecule is packaged into thread-like structures called chromosomes.
- Each chromosome is made up of DNA tightly coiled many times around proteins called histones that support its structure.
- Chromosomes come in pairs. Normally, each cell in the human body has 23 pairs of chromosomes (46 total chromosomes).
- Half come from the mother; the other half come from the father.
- Sex determination: Two of the chromosomes (the X and the Y chromosome) determine sex as male or female when you are born. They are called sex chromosomes:
- Females have 2 X chromosomes: The mother gives an X chromosome to the child.
- Males have 1 X and 1 Y chromosome: The father may contribute an X or a Y. The chromosome from the father determines if the baby is born as male or female.
- The remaining chromosomes are called autosomal chromosomes. They are known as chromosome pairs 1 through 22.
|

