Context
Vertical Launch Short Range Surface to Air Missile (VL-SRSAM) has been successfully flight-tested by Defence Research & Development Organisation (DRDO) and the Indian Navy from an Indian Naval Ship at Integrated Test Range (ITR), Chandipur off the coast of Odisha.
What is VL-SRASAM?
- The VL-SRSAM, a ship borne weapon system.
- VL-SRSAM has been designed and developed jointly by three facilities of the Defence Research and Development Organisation for deployment of Indian Naval warships.
- It is meant for neutralising various aerial threats at close ranges at close ranges including sea-skimming targets.
- The tactic of sea skimming is used by various anti-ship missiles and some fighter jets to avoid being detected by the radars onboard warships.
- For this, these assets fly as close as possible to sea surface and thus are difficult to detect and neutralise.
|

India’s Guided Weapon Program
|
The design of VL-SRSAM
- The missile has been designed to strike at the high-speed airborne targets at the range of 40 to 50 km and at an altitude of around 15 km.
- DRDO officials have said its design is based on Astra missile which is a Beyond Visual Range Air to Air missile.
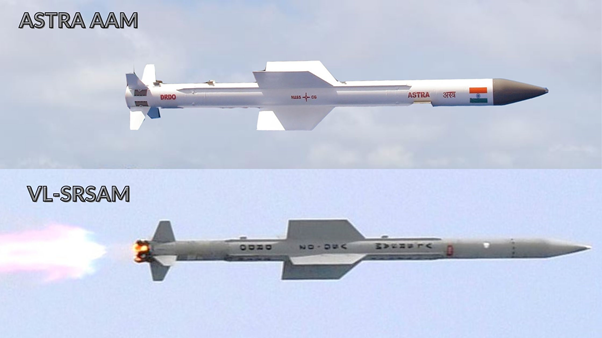
- Two key features of the VL-SRSAM are cruciform wings and thrust vectoring.
- Cruciform wings: The cruciform wings are four small wings arranged like a cross on four sides and give the projective a stable aerodynamic posture.
- Thrust vectoring: The thrust vectoring is an ability to change the direction of the thrust from its engine control the angular velocity and the attitude of the missile
|
Astra Missile
- Astra is a Beyond Visual Range (BVR) class of air-to-air Missile (AAM) system designed to be mounted on fighter aircraft.
- The missile has been designed and developed by the Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) for deployment on fighter jets like Sukhoi-30 MKI and Tejas of the IAF and the Mig-29K of the Navy.

|