Seat belts, Air bags, and Safety Regulations:
- Posted By
10Pointer
- Categories
Polity & Governance
- Published
10th Sep, 2022
-
-
Context
The untimely demise of former Tata Group Charmain Cyrus Mistry in an accident has brought into the limelight the importance of safety features like seat belts and airbags. It also highlights the state of road safety regulations in India.
-
Data related to Road Accidents:
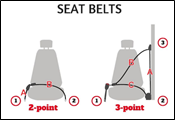
About Seat Belts:
- Seat belts had been around, if infrequently used, since the 19th Many street cars had lap belts in the 1930s, but few people used them.
- These early lap belt models kept passengers from flying out of the car but did nothing to protect their heads or torsos.
Present days seat belts:
- In 1959, Volvo engineer Nils Bohlin developed the modern three-point seat belt or Y-shaped seat belt.
- It is now standard in cars sold in India.
- This new model secured the chest and hips with a single belt.
- These seatbelts became mandatory in all new United States vehicles in 1968.
Threats of not wearing the seat belt:
- At moderate to high speeds, the driver or passenger who has no seat belt continues to move forward at the speed of the vehicle (due to moment of inertia).
- In such cases the motion of the occupants in the car doesn’t stop until some object stops the occupant, for example:
- Occupants colliding with internal objects in the car.
- Being ejected through the front windscreen during the collision.
Airbags:
- Airbags are inflatable cushions built into a vehicle that protect occupants from hitting the vehicle interior or objects outside the vehicle (for example, other vehicles or trees) during a collision.
- If the crash is severe enough, the sensors signal inflators to fill the bags with gas in a fraction of a second.
- Dual airbags (driver and passenger) became mandatory on all vehicles this January.
- A driver airbag has been compulsory for all passenger vehicles since July 1, 2019.

What are the rules on airbags elsewhere in the world?
- United States: Front airbags are required by law in all cars. But most carmakers offer between six and 10 airbags.
- Europe: Almost every new car sold in Europe is equipped with front and side airbags. In the EU and the United Kingdom, there is no direct legal requirement for new cars to feature airbags.
Other Safety Features:
Head Restraints:
- Head restraints, which are found either as adjustable models or molded into the seats, are used to prevent injury from the sudden extreme movement of the neck.
Car brake fluid:
- Brake fluid is the liquid chemical solution used in the hydraulic braking systems of modern cars. It is designed to amplify your foot's force on the brake pedal and turn it into pressure on your car's brakes. Without brake fluid, it would take a lot more than just your foot to stop your car.
- It needs a constant viscosity across wide temperature ranges (viscosity refers to how thick a liquid is and how easily it flows).
- Most brake fluids are either glycol- or silicone-based, and the two types should never be mixed.
Anti-Lock Braking System (ABS):
- The ABS is a protective and anti-skid braking system used on land vehicles like bikes, trucks, buses, etc.
- It avoids the tires of a vehicle from locking up & skidding when brakes are applied on emergency shutdown.
- The Centre had made fitment of ABS mandatory for manufacturers from April 2019.
Speed Alert System:
- Once the car crosses the speed of 80 km/hr, this system sends out an alert every 60 seconds and starts beeping continuously at speeds above 120 km/hr.
- The system is designed to reduce speeding, and cannot be overridden or turned off.
Reverse Parking Sensors:
- The sensors are activated when the reverse gear is engaged, and they give out a warning if there are obstructions in the path of the reversing car.
- The system helps prevent collisions with objects that might not be visible in the car’s mirrors.
-
How does India regulate and enforce safety?
- The Ministry of Road Transport and Highways has recently approved the draft General Statutory Rules notification to introduce Bharat NCAP (New Car Assessment Programme).
- It introduces the concept of the safety rating of passenger cars and empowers consumers to take informed decisions.
- NCAP will be rolled out from 1st April 2023.
- Auto manufacturers in India as well as importers will have the option of getting cars star rated within the country.
- The USA was the first country to introduce a program for testing the safety standards of a car through crash tests.
About Bharat NCAP Rating:
- The proposed Bharat NCAP assessment will allocate Star Ratings from 1 to 5 stars. The testing of vehicles for this programme will be carried out at testing agencies, with the necessary infrastructure.
- The vehicle shall be assigned a star rating from one to five stars, based on scoring against various tests undertaken as per Automotive Industry Standard (AIS)-197.
- Bharat NCAP rating will be based on the evaluation of the vehicle in the areas of
- Adult Occupant Protection (AOP)
- Child Occupant Protection (COP)
- Safety Assist Technologies (SAT)
- Ministry of Road Transport and Highways issued a draft notification providing for three-point seat belts to be provided in all vehicles coming under the M1 category manufactured after October 1st,
- According to Rule 38 (3) of the Central Motor Vehicle, a person "seated in the front seat or the persons occupying front facing rear seats" is required to wear a seat belt.
M1 Category of Vehicle:
- According to the government’s homologation rules, vehicles are bucketed into broad categories.
- ‘Category M’ covers motor vehicles with at least four wheels, used for carrying passengers.
- Sub-category ‘M1’ defines “a motor vehicle used for the carriage of passengers, comprising not more than eight seats in addition to the driver’s seat”.
-
What is Homologation?
- Homologation is the process of certifying that a particular vehicle is roadworthy, and matches certain specified criteria laid down by the government for all vehicles that are built or imported into the country.
Road safety initiatives under Motor Vehicles Amendment Act 2019:
- Vehicle Fitness: Automated fitness testing for vehicles has been made mandatory.
- Recall of Vehicles: The Act allows the central government to order for recall of motor vehicles if a defect in the vehicle may cause damage to the environment, or the driver, or other road users.
- Road Safety Board: A National Road Safety Board will be created to advise the central and state governments on all aspects of road safety and traffic management.
- Protection of Good Samaritan: The Act lays down the guidelines and provides rules to prevent harassment of Good Samaritan to encourage people to help road accident victims.
- Cashless Treatment during Golden Hour: The Act provides for a scheme for cashless treatment of road accident victims during golden hour.
- Motor Vehicle Accident Fund: To provide compulsory insurance cover to all road users in India which will be utilized for: treatment of persons injured in road accidents as per the golden hour scheme.

