NASA is sending ‘water bears’ to the International Space Station
- Posted By
10Pointer
- Categories
Science & Technology
- Published
7th Jun, 2021
-
-
Context
After successfully figuring out ways to water plants in outer space, NASA is now all set to send glow-in-the-dark baby squids and about 5,000 tardigrades, also called water bears, to the International Space Station.
-
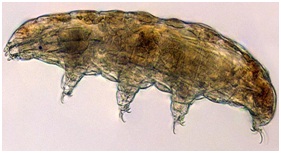
What are Tardigrades?
- Tardigrades, also known as water bears, are known to tolerate environments more extreme than most life forms are able to.
- These tiny animals (around 1mm long) have a common habitat in water and are a model organism for studying biological survival under extreme conditions on Earth and in space.
- Studies in microgravity on living organisms could advance the understanding of stress factors affecting humans in space and support the development of countermeasures.
- Researchers will look to study how tardigrades survive and reproduce in these environments, and whether those biological processes can be replicated in humans or not.
|
Euprymna scolopes
- Apart from water bears, Nasa is also sending bobtail squid, Euprymna scolopes, an animal model that is used to study symbiotic relationships between two species.
- Humans rely on microbes to maintain a healthy digestive and immune system, but we do not understand the complex symbiotic system.
|
-
Previous experiments
- While this is the maiden space voyage for bobtail squid, it isn't the first time tardigrades have launched into space or even visited the ISS.
- A 2007 European Space Agency mission sent tardigrades into low-Earth orbit, and then Italian scientists launched the creatures to the space station again in 2011.
- Most recently, an Israeli spacecraft was carrying a horde of tardigrades when it crashed on the moonin 2019, possibly killing them.
-
What are the reasons behind the experiment?
- The new set of arrivals to the flying laboratory beyond Earth's orbit will push the envelope on experiments that include
- studying how water bears tolerate extreme environment
- whether microgravity affects symbiotic relationships
- analysing the formation of kidney stones
- The water animals could prove helpful in designing new strategies and improved protective measures for astronauts as Nasa returns to the Moon and looks at long-duration space travel to Mars.
- The new arrivals are part of the 22nd SpaceX cargo resupply mission.
|
22nd SpaceX cargo resupply mission
- This 22nd contracted resupply mission for SpaceX delivers the new ISS Roll-out Solar Arrays (iROSA) to the space station in the trunk of the Dragon spacecraft.
- The robotic Canadarm2 will extract the arrays and astronauts will install them during spacewalks planned for June 16 and 20.
|
-
How would it be done?
- The water bears and bobtail squid will be involved in experiments aboard the floating laboratory, and will be arriving in a semi-frozen state before they are thawed out, revived and grown in a special bioculture system.
- One of these studies involves looking at how the water bears would behave in a spaceflight environment.
- Researchers will be able to study their hardiness close up, and possibly identify the genes that allow them to become so resilient.
- Scientists also want to look at how microgravity conditions affect the relationship between the bobtail squid –which are also tiny (3 mm long) – and beneficial microbes, as part of a study called Understanding of Microgravity on Animal-Microbe Interactions (UMAMI).
-
What are the benefits of such study?
- Better arrangement for astronauts: By learning how the water bears can survive in low gravity conditions, it would be possible to design better techniques to keep astronauts healthy on long-duration space missions.
- Better understanding: Microbes play a crucial role in the normal development of animal tissues and in maintaining human health, and the research will allow scientists to have a better understanding of how beneficial microbes interact with animals when there is a lack of gravity.
- Better human health and well being: In the human body, microorganisms contribute to a variety of functions, including digestion, developing the immune system and detoxifying harmful chemicals. A disruption in our relationship with these microbes can lead to disease. Scientists might find ways to protect and even enhance the complex relationship between animals and beneficial microbes, ensuring better human health and well being.
-
About the International Space Station (ISS)
- The International Space Station (ISS) is a large spacecraft. It orbits around Earth. It is a home where astronauts live.
- The space station is also a science lab. Many countries worked together to build it.
- The ISS has been in space since 1998, and has been known for the exemplary cooperation between the five participating space agencies that run it:
- NASA (United States)
- Roscosmos (Russia)
- JAXA (Japan)
- ESA (Europe)
- CSA (Canada)
-
Conclusion
NASA believes that this research may lead to important breakthroughs. In space, the findings will help space agencies develop better measures to protect astronauts from adverse host-microbe alterations on long-duration missions.
