Context
In the recent years, there is an ‘insect apocalypse’ underway across the world. Insects have declined by 75% in the past 50 years – and the consequences may soon be catastrophic.
What is insect?
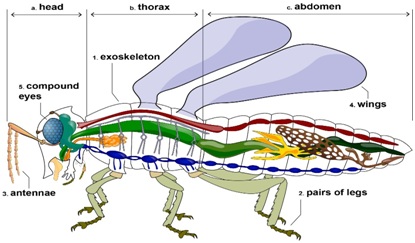
- Any small creature with six jointed legs and a body divided into three parts namely head, thorax and abdomen is known as an ‘insect’.
- They have wings, two antennae and an exoskeleton. Ants, bees and flies are insects.
- ‘Entomology’ is the scientific study of insects, a branch of zoology.
- There may be as many as 10 million species of insects including:
- 3, 60,000 species of beetle
- 1, 80,000 species of butterfly and moth
- 1, 20,000 fly species
- 1, 10,000 species of bees, wasps and ants
- 82,000 true bug species (cicadas, aphids, mealy bugs, etc)
- 20,000 species of grasshoppers
- 5,000 dragonfly species
- 2,000 praying mantis species
Threats causing insect apocalypse
- Habitat loss
- Climate change
- Particulate Matter
- Land-use change
- Insecticides
- Light pollution
- Invasive species
- Flowers release odour as chemicals called volatile organic compounds, which help insects locate flowers.
- Pollutants could react with and change the scents of flowers, making them harder to find.
|
Why insects matter?
Insects have an essential role to play in the ecosystem.
- Crop productivity: They pollinate many of fruits, flowers and vegetables, contributing significantly to the productivity of at least 75 per cent of global crop species.
- Food security: Their services are vital for India’s food security.
- Pest control: Insects keep pests in check. For example-
- Ladybird preys on aphids that damage crops.
- Insects such as ladybird beetles, lacewings, parasite wasps, etc, control other insects, arthropods and vertebrates.
- Food source: Insects are also food sources for amphibians, reptiles, birds and mammals.
- Economic significance: Insects have economic importance as well. They provide honey, silk, wax and other products.
