At Ramagundam in Telangana's Peddapalli district, the country's largest floating solar power facility, spanning more than 600 acres, is now completely operational.
|
Key Facts:
|

India’s status on Floating solar project:
|
Key Facts:
|
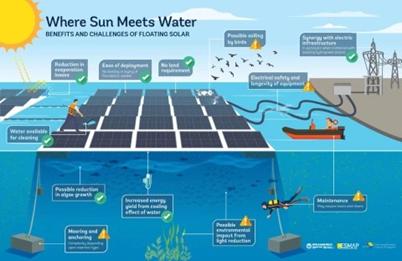
Floating solar projects provides an edge over other source of energy and also over solar projects installed over land and rooftop. Implementing such ambitious project will help India to gain a global leadership in the renewable energy domain. Success of the project depends on the execution methodology and how government crosses the technical barriers and also how efficiently it can mitigate the future climate challenges.
Verifying, please be patient.