Introduction
The Antarctic and Arctic regions are polar opposites in more ways than one. These two regions have differences in the volume of ice, their climate, their seasonality, and much more. One important feature which separates the Arctic and Antarctic regions is their sea ice and in particular how it changes over the year and its extent.
Let us answer a few questions related above-mentioned points of discussion.
Significance of sea ice and sea-level rise
- Sea ice is frozen seawater that floats on the ocean’s surface surrounding the Arctic and Antarctic regions.
- Sea ice also interacts with the climate system.
- It helps with the heat exchange between the atmosphere and the polar regions.

Interesting Facts:
- The white surface colour of the sea ice means it has a high reflective index causing most of the sun’s incoming solar radiation to be reflected back out to space.
- This keeps the polar regions cool. It also interacts with the ocean currents which help distribute heat around the globe.
What are the differences between the two regions?
|
Arctic
|
Antarctica
|
- The sea ice extent in the Arctic region covers the highest latitudes. It surrounds Greenland, the northernmost coast of Canada, Russia, and the High Arctic during the winter months.
- Sea ice in the Arctic region changes seasonally.
- During the winter, as temperatures decrease the seawater freezes and eventually reaches its maximum extent in March.
- It then melts during the summer and reaches its minimum extent in September.
|
- Antarctica is surrounded completely by the ocean. Because of this, the sea ice forming in the winter months is not constrained by surrounding landmasses, unlike the Arctic.
- This allows the sea ice to spread over a much larger area.
- Much of the sea ice which has built up in the winter months (March to September) is melted in the summer, leaving only isolated areas in the Weddell and Ross Seas.
- The maximum sea ice extent in the Antarctic region peaks from September to October.
|
What is the difference between sea ice and glaciers?
- Sea iceforms and melts strictly in the ocean whereas glaciers are formed on land.
- Icebergs are chunks of glacial ice that break off glaciers and fall into the ocean.
- When glaciersmelt, because that water is stored on land, the runoff significantly increases the amount of water in the ocean, contributing to global sea level rise.
- Sea ice, on the other hand, is often compared to ice cubes in a glass of water: when it melts, it does not directly change the level of water in the glass.
Reasons for difference in pace of ice-melting
- Due to Geographical reasons:
- Seasonal Variations: Some differences in seasonal sea ice extent between the Arctic and Antarctic are due to basic geography and its influence on atmospheric and oceanic circulation.
- Topography: The Arctic is an ocean basin surrounded largely by mountainous continental land masses, and Antarctica is a continent surrounded by ocean.
- In the Arctic, sea ice extent is limited by the surrounding land masses.
- In the Southern Ocean winter, sea ice can expand freely into the surrounding ocean, with its southern boundary set by the coastline of Antarctica.
- Because Antarctic Sea ice forms at latitudes further from the South Pole (and closer to the equator), less ice survives the summer.
- Hemispheric differences: Sea ice extent in both poles changes seasonally; however, longer-term variability in summer and winter ice extent is different in each hemisphere, due in part to these basic geographical differences.
- Due to Oceanic influence:
- Arctic ice is thicker and stays frozen longer during summer. The Antarctic is almost the geographic opposite of the Arctic - not just because it's on the other side of the world.
- The Antarctic consists of land surrounded by an ocean. The sea ice is free to move and often floats northward into warmer waters, which eventually melts during the southern hemisphere's summer months.
What are the similarities in both regions?
Common misconceptions concerning polar region comparison:
- Polar bears and penguins occupy the same habitat.
- Both poles are similar in temperature.
- Both the Arctic and Antarctic are solid ice, with snow on top.
- Antarctica is quite a small continent that nobody can visit.
- Humans cannot live in the
- Polar oceans are too cold for most life.
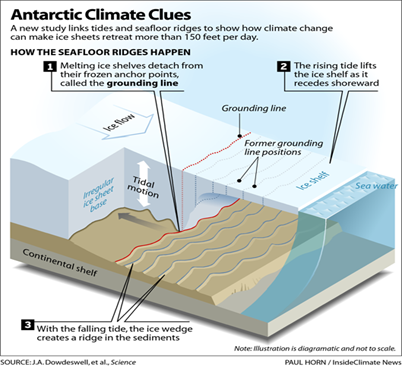
Future challenges in both the region
- Faster Ice melting: Anthropogenic climate change will have effects on global sea ice. The IPCC Special Report on the Oceans and Cryosphere has shown how these trends are likely going to continue into the future.
- The impact of climate change on the Arctic is more linear than in the Antarctic. In the Arctic, there is a clear relationship between the increasing temperatures and decreasing sea ice.
- However, the impact on Antarctic Sea ice is slightly more complex due to lots of interacting systems.
- Effect on Marine life: The decline in sea ice will continue to have notable implications for marine wildlife. The IPCC showed how in the Arctic, predictions for many marine mammals and birds are going to likely decline in the future, threatening populations. But there are also concerns that populations of some sub-Arctic fish species will continue to increase, adding more stress on an already delicate ecosystem.
- Terrestrial life of Antarctica: In Antarctica, there is also a clear threat to species that depend on sea ice. Most significant is the effect that the decline in sea ice will have on krill.
Conclusion
Because the cryosphere - the icy part of our planet - is so interconnected with other parts of the Earth system, what happens in the cryosphere affects the whole Earth. As climate change causes the temperature to rise, ice melts. Much of this ice is in the Arctic and Antarctic, but the planet as a whole is affected by changes in these polar regions as ice melts. So what happens in the cryosphere does not stay in the cryosphere.

