Climate change triggering global collapse in insect numbers: Study
- Posted By
10Pointer
- Categories
Science & Technology
- Published
30th Apr, 2022
-
-
Context
The new study, published in Nature, finds that climate-stressed farmland possesses only half the number of insects, on average, and 25 percent fewer insect species than areas of natural habitat.
-
What is insect?
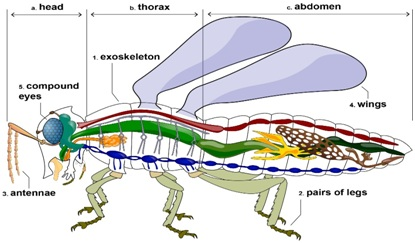
- Any small creature with six jointed legs and a body divided into three parts namely head, thorax and abdomen is known as an ‘insect’.
- They have wings, two antennae and an exoskeleton. Ants, bees and flies are insects.
- ‘Entomology’is the scientific study of insects, a branch of zoology.
- There may be as many as 10 million species of insects including:
- 3, 60,000 species of beetle
- 1, 80,000 species of butterfly and moth
- 1, 20,000 fly species
- 1, 10,000 species of bees, wasps and ants
- 82,000 true bug species (cicadas, aphids, mealy bugs, etc)
- 20,000 species of grasshoppers
- 5,000 dragonfly species
- 2,000 praying mantis species
- The largest of the 29 major insect groups are butterflies/moths, beetles, bees/wasps/ants and flies.
- Each of these groups is thought to contain more than one million species.
- Knowledge gap: 80% of insects may not have been discovered yet – of which many are tropical species.
|
Key findings of the study:
- Study area: Some three-quarters of a million samples from around 6,000 sites worldwide were analysed in study, adding up to nearly 20,000 different species in all.
- Insect declines are greatest in farmland areas within tropical countries– where the combined effects of climate change and habitat loss are experienced most profoundly.
- The farmland sites possess only half the number of insects, on average, and more than 25 per cent fewer insect species.
- Throughout the world, farmland in climate-stressed areas where most nearby natural habitat has been removed has lost 63 per cent of its insects, on average, compared with as little as 7 per cent for farmland where the nearby natural habitat has been largely preserved.
- It is predicted that climate change will have a particularly big impact in the planet’s tropical regions.
- Temperatures in the tropics are naturally quite stable, so species aren’t used to coping with the fast changes in temperature we are seeing with climate change.
-
Understanding ecological importance of insects:
- Natural cleaner: Insects are critical to the future of our planet. They help to keep pest species under controland break down dead material to release nutrients into the soil.
- Key-pollinators: Flying insects are also key pollinators of many major food crops, including fruits, spices.
- Eighty-seven of the world’s major crops are thought to be fully or partially dependent on insect pollinators,of which most tend to be grown in the tropics.
- Cocoa, for example, is primarily pollinated by midges, a group of flies infamous for bedevilling camping trips in Scotland and other parts of the northern hemisphere.
- In fact, midges play a vital and under-appreciated role in pollinating the cocoa needed to make chocolate.
- Flowers release odour as chemicals called volatile organic compounds, which help insects locate flowers.
- Pollutants could react with and change the scents of flowers, making them harder to find.
|
- Diversified role: Insects are important because of their diversity, ecological role, and influence on agriculture, human health, and natural resources.
- Biological foundation: Insects create the biological foundation for all terrestrial ecosystems.
- They cycle nutrients, pollinate plants, disperse seeds, maintain soil structure and fertility, control populations of other organisms, and provide a major food source for other taxa.
- Food security:Their services are vital for India’s food security.
- Pest control:Insects keep pests in check. For example-
- Ladybird preys on aphids that damage crops.
- Insects such as ladybird beetles, lacewings, parasite wasps, etc, control other insects, arthropods and vertebrates.
- Food source:Insects are also food sources for amphibians, reptiles, birds and mammals.
- Economic significance:Insects have economic importance as well. They provide honey, silk, wax and other products.
-
Reason behind the decline
- Dual threats: Insects are facing an unprecedented threat due to the “twin horsemen” of climate change and habitat loss.
- Habitat loss: Habitat loss can add to the effects of climate change by limiting available shade, for example, leading to even warmer temperatures in these vulnerable areas.
- Light pollution:Light pollution threatens the insects’ survival.
- Others:
- Particulate Matter
- Land-use change
- Insecticides
- Invasive species
-
Impact of loss of insects
- Loss of insect biodiversity could put these vital ecological functions at risk, threatening human livelihoods and food security in the process.
- There are some places in China where the loss of insects is so great that armies of people have been told to fan out and go through orchards with paint brushes and feathers on sticks to pollinate crops by hand.
- It is a hugely labor intensive operation that obviously isn't really sustainable long-term.
|
A world without the internet would be difficult but livable. The same can’t be said for a world without insects.
