Chandigarh, first in the race to assess the carbon footprint of individuals
- Posted By
10Pointer
- Categories
Environment
- Published
25th Feb, 2021
-
-
Context
Chandigarh became the first state or Union Territory in India to launch Carbon Watch, a mobile application to assess the carbon footprint of an individual.
-
Background
- India is among the fastest-growing economies and the third largest emitting country in the world.
- However, India’s CO2 emissions have doubled since 2005, driven by various reasons. The trend in India’s CO2 emissions is of global importance.
- India carbon (Co2) emissions for 2016 was 2,407,671.53, a 2.99% increase from 2015
- India carbon (Co2) emissions for 2015 was 2,337,749.17, a 4.7% increase from 2014
- India carbon (Co2) emissions for 2014 was 2,232,729.96, a 9.93% increase from 2013
- India carbon (Co2) emissions for 2013 was 2,030,971.62, a 0.85% increase from 2012
|
- The country has the most vulnerable population, which will be impacted by climate change and would need protection.
- With increasing extreme-weather events and threats of global warming, it is time to prepare for climate change on a war footing and bring adaptation to focus in the climate discourse.
- In this regard, this latest development is a welcome step and it shows that India is on the rights track.
- It’s time for climate diplomacy by India.
-
Analysis
What is Carbon Watch?
- Carbon Watch is a mobile app for city residents to assess their carbon footprints.
- The app focuses on individuals’ actions and calculates carbon footprint based on transport, energy, waste, and water consumption.
- Objective: To reduce it to make them climate-smart citizens.
- Developed by: Department of Environment and Forest.
- It also suggests remedial actions and sensitizes people about their lifestyle emissions, their impact, and possible countermeasures to mitigate the same.
- The initiative will help keep the city and the country at the vanguard of the initiatives to protect the climate.
-
How will it work?
- As a person downloads the application, they will need to fill details in four parts — Water, Energy, Waste Generation, and Transport (Vehicular movement).
- Water: In the category of Water, the person will be required to inform about the consumption of water.
- Energy: In the Energy category, the details regarding the electricity units consumed every month at the house, monthly bill, etc, and usage of solar energy will have to be furnished.
- Waste: In the Waste category, the individual will need to inform about the waste generated on their part and their family.
- Transport: In the transport section, the individual will have to inform about the mode of transport used by them- four wheeler, two-wheeler or bicycle.
-
What is carbon footprint?
- A carbon footprint is the total amount of greenhouse gases (including carbon dioxide and methane) that are generated by our actions.
- It includes carbon dioxide — the gas most commonly emitted by humans — and others, including methane, nitrous oxide, and fluorinated gases, which trap heat in the atmosphere, causing global warming.
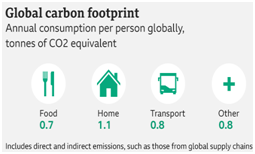
|
According to WHO, a carbon footprint is a measure of the impact your activities have on the amount of carbon dioxide (CO2) produced through the burning of fossil fuels and is expressed as a weight of CO2 emissions produced in tonnes.
|
Recent Government efforts to address climate change
- National Action Plan on Climate Change (NAPCC): It covers eight major missions on Solar, Enhanced Energy Efficiency, Sustainable Habitat, Water, Sustaining the Himalayan Ecosystem, Green India, Sustainable Agriculture and Strategic Knowledge on Climate Change
- International Solar Alliances (ISA)
- State Action Plan on Climate Change (SAPCC)
- FAME Scheme – for E-mobility
- Atal Mission for Rejuvenation & Urban Transformation (AMRUT) – for Smart Cities
- Pradhan Mantri Ujjwala Yojana – for access to clean cooking fuel
- UJALA scheme - for embracing energy-efficient LED bulbs
- Swachh Bharat Mission
|
Paris Agreement
- India has pledged under the Paris Agreement to reduce the carbon intensity of its economy by 33-35% by 2030, compared to 2005 levels.
|
Measures to reduce carbon footprints

Significance of mapping carbon footprint
- It helps to prepare for future environmental legislation
- Manage carbon risk exposure and identify areas for improvement will become easy
- It will improve efficiency and cut costs through reduced energy consumption
- It helps to motivate and engage citizens by involving them in carbon reduction plans
-
Conclusion
To decrease the carbon footprints, India needs to remain on track and for this, it needs consistent ‘challengers’ whether in the form of an empowered and aware population or through a grassroots movement that informs the national policy while demanding sustainable and healthy growth for the country.

