Context
- Studies have shown that using the same adenovirus subtypes for repeated vaccination might result in reduced efficacy.
What is an Adenovirus antibody?
- Adenoviruses(family Adenoviridae) are medium-sized (90–100 nm)viruses.
- They are-enveloped (without an outer lipid bilayer) viruses.
- They are icosahedral nucleocapsid containing a double-stranded DNA genome.
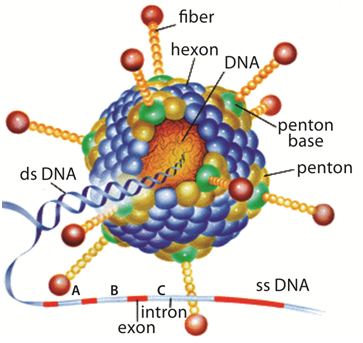
- Adenoviruses: These are a group of common viruses that infect the lining of the eyes, airways, and lungs, intestines, urinary tract, and nervous system.
- They're common causes of fever, coughs, sore throats, diarrhea, and pink eye.
- The immune system generated against the adenovirus infection causes the antibodies formation.
How these antibodies illicit response action against vector-based vaccine?
- Pre-existing antibodies cause the relatively low efficacy of the adenovirus-based vaccine in some people.
- It affects the development of antibodies against the new target.
- Pre-existing antibodies against adenoviruses will stop the adenovirus particles from getting into cells and making the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein they carry the code for.
Adenovirus as Vector
- Adenoviruses are excellent vectors for delivering genes or vaccine antigens. Adenovirus-based vectors offer several advantages over other viral vectors such as:
- a broad range of tissue tropism
- well-characterized genome
- ease of genetic manipulation including acceptance of large transgene DNA insertions
- inherent adjuvant properties
- ability to induce robust transgene-specific T cell and antibody responses
- non-replicative nature in host
- ease of production at large scale
Vector-based Vaccines
- Viral vectors are tools commonly used to deliver genetic material into cells.
- This process can be performed inside a living organism (in vivo) or in cell culture (in vitro).
- As a medium of transport: Viruses have evolved specialized molecular mechanisms to efficiently transport their genomes inside the cells they infect.
- Functioning: They are then inserted into the genome of a non-pathogenic organism, where they are expressed on the organism's surface and can elicit an immune response.
